Here's a breakdown of 1 Enoch, also known as the Ethiopic Book of Enoch, including historical background, structure, dating, and influence:
📘 Overview of 1 Enoch
1 Enoch is an ancient Jewish apocalyptic text traditionally attributed to Enoch, the seventh from Adam (Genesis 5:21–24). Though not part of the canonical Bible in most traditions, it was highly influential in Second Temple Judaism and early Christianity.
🕰️ Date of Composition
1 Enoch is not a single unified book but a composite work, written over several centuries. Most scholars date its various sections between 300 BC and 100 BC, though some parts may have earlier oral traditions.
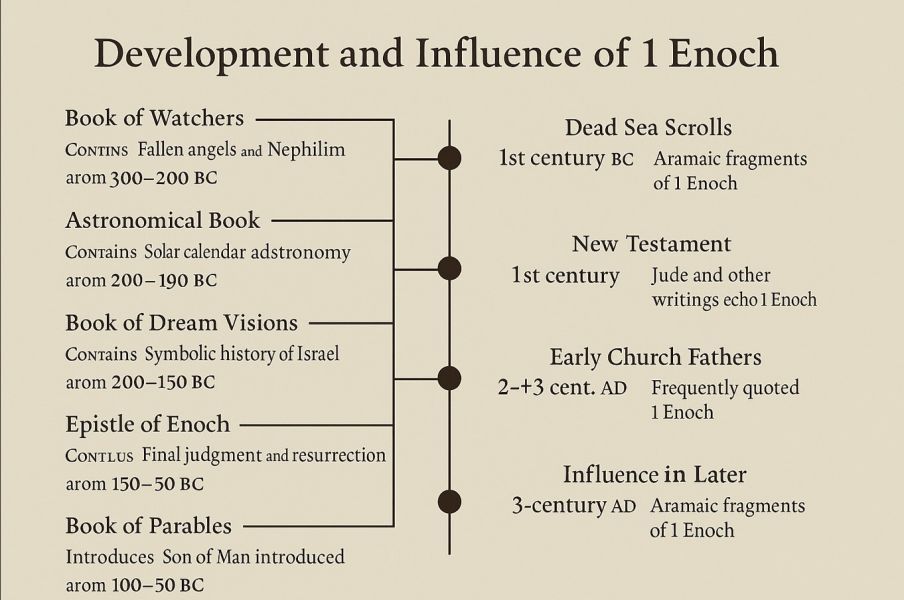
| Section | Approx. Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Book of the Watchers (Ch. 1–36) | c. 300–200 BC | Earliest section; about fallen angels and the Nephilim. |
| Book of Parables (Ch. 37–71) | c. 100–50 BC | Introduces the “Son of Man” figure. |
| Astronomical Book (Ch. 72–82) | c. 300–200 BC | Contains a solar calendar and astronomy. |
| Book of Dream Visions (Ch. 83–90) | c. 200–150 BC | Symbolic history of Israel. |
| Epistle of Enoch (Ch. 91–108) | c. 150–50 BC | Prophecies of final judgment and resurrection. |
🌍 Language and Manuscripts
-
Original language: Likely Aramaic, with some parts possibly in Hebrew.
-
Preserved in: Complete form in Ge'ez (Classical Ethiopic).
-
Fragments found: Among the Dead Sea Scrolls (Qumran, Cave 4) in Aramaic, confirming its ancient Jewish origin.
🏛️ Canonical Status
| Tradition | Status |
|---|---|
| Ethiopian Orthodox Church | Canonical – Part of their Bible. |
| Jewish Rabbinic Tradition | Rejected – Not included in Tanakh. |
| Western Christianity | Apocryphal – Not in Protestant or Catholic Bibles. |
| Early Disciples | Frequently referenced (e.g., Jude, early Church Fathers). |
✍️ Authorship
Though attributed to Enoch, son of Jared (Genesis 5), the book is pseudepigraphal, meaning it was written under a revered name to lend authority. It reflects Jewish apocalyptic and wisdom traditions from the Second Temple era.
🔑 Key Themes
-
Fallen angels (Watchers) and the Nephilim (Gen 6:1–4 elaboration)
-
The coming judgment of the wicked and reward of the righteous
-
The Son of Man / Elect One – a messianic and eschatological figure
-
Cosmic visions of heaven, hell, and the afterlife
-
Solar calendar and opposition to lunar calendar sects (like the Pharisees)
✒️ Influence on the New Testament
-
Jude directly quotes Enoch.
-
Concepts like the Son of Man, final judgment, resurrection, and angels are echoed in Revelation, Matthew, 1 Peter, and 2 Peter.
-
Enoch was popular among early Disciples and quoted by writers like Tertullian, who considered it inspired.